Sterility!! The one word that can give nightmares to many Life Sciences students. It doesn’t spare even the best of lab assistants. It can take
Tag: Microbiology
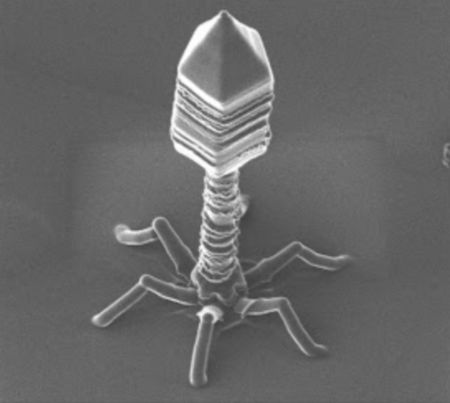
Bacteriophage literally means bacteria eater, because they infect bacteria and kill them. It means bacteria are host to the bacteriophage. Like other viruses, bacteriophages are
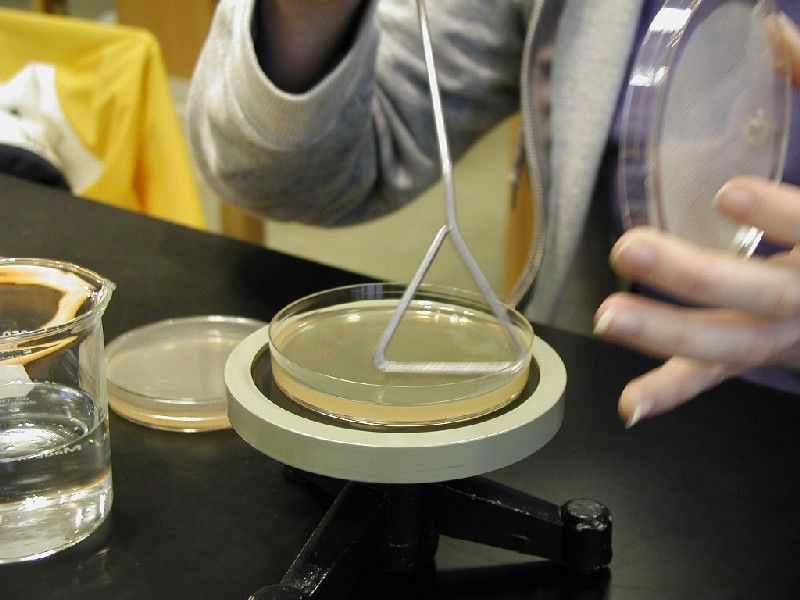

What is Pure (Axenic) culture? It is laboratory microbial culture which contains only one specific species of microorganism. Why do we need it? Microorganisms are
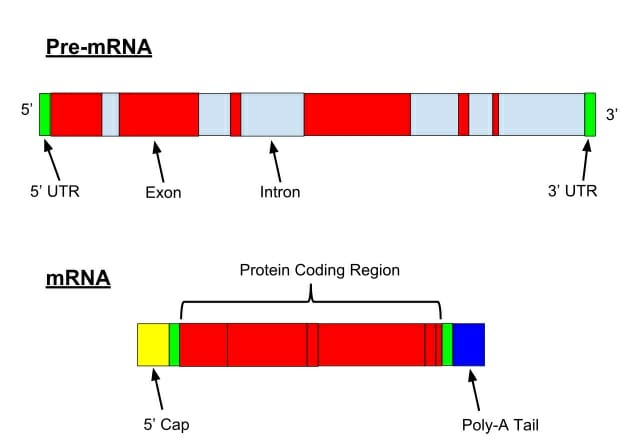
In central Dogma of life, we have studied that DNA replication, transcription and translation are vital molecular processes. In Eukaryotes, the transcription is followed by
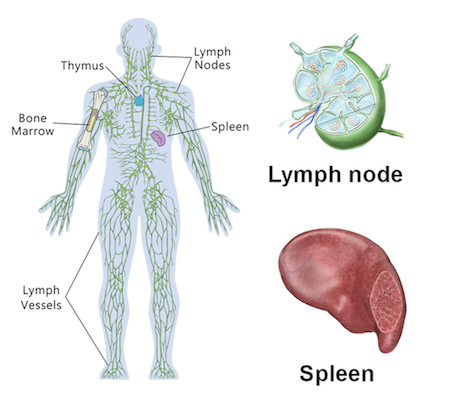
Lymphoid organs are of two types – Primary and Secondary. They are classified based on their function. The Immune system is like an organization of

Dye Reduction tests are used to check the microbial load present in the milk sample. It is convenient and quick to use. AIM:- To carryout
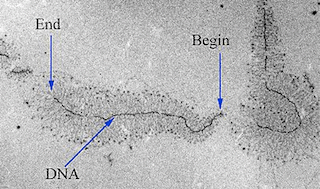
Transcription is the first step for protein synthesis. It is the process by which the m-RNA is synthesized and the information is transferred from nucleus

Cloning is a method of producing genetically identical organism that already exist in nature. It is asexual form of reproduction. There is no involvement of
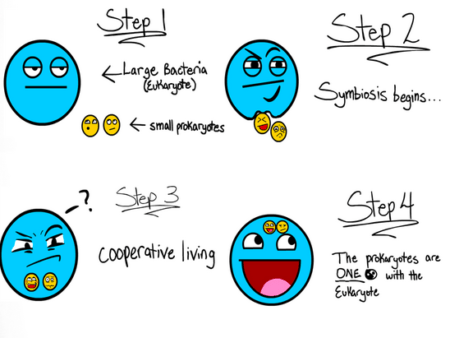
Endosymbiosis explains the origin of chloroplast and mitochondria. The life was initiated on earth, around 3.5 billion years ago. The first life form was a
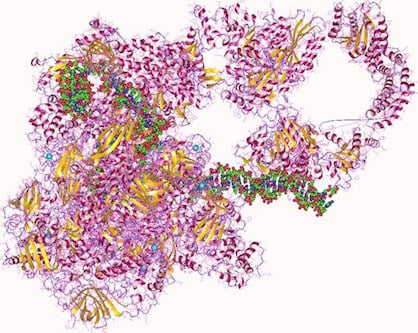
Introduction – Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from DNA, catalysed by a very special enzyme, RNA polymerase (RNAP). The DNA in the gene is
