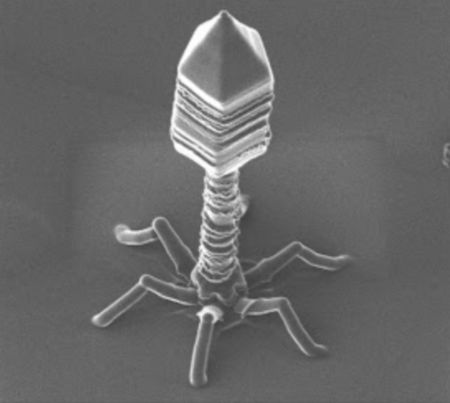
Bacteriophage literally means bacteria eater, because they infect bacteria and kill them. It means bacteria are host to the bacteriophage. Like other viruses, bacteriophages are
Tag: Bacteria
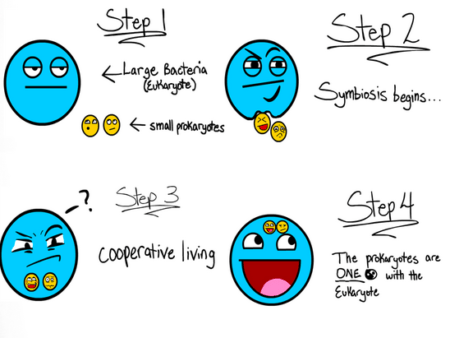
Endosymbiosis explains the origin of chloroplast and mitochondria. The life was initiated on earth, around 3.5 billion years ago. The first life form was a
Bacteria belongs to prokaryotes and hence it lacks nucleus and membrane bound organelle. But it has sufficient organelles that maintains and regulated important physiological, biochemical
Archaebacteria are fascinating microbes and show diverse characteristics. They are unicellular and do not have nucleus and hence scientist thought to categorize them in prokaryotes.
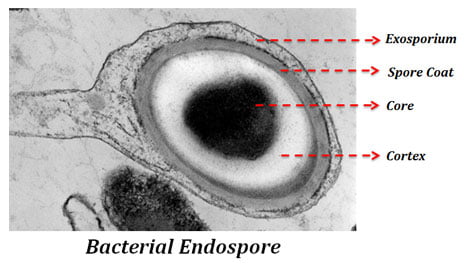
Endospore is the resistant form of bacteria which is very difficult to kill. Sporulation: Sporulation is a spore forming process in bacteria. Spores are metabolically
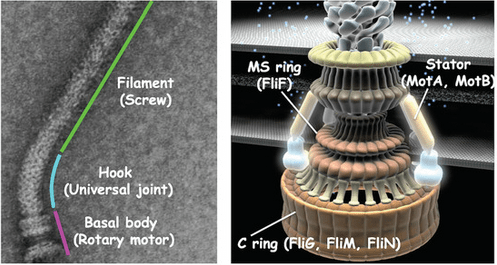
Flagella is the motility organelle of the bacteria. Introduction: Flagella is known as motility or locomotor organelle and it looks hair like appendage. They are

Why bacteria are microscopic? It is a vital question that comes to our mind. This article explains the relationship between size of the bacteria and
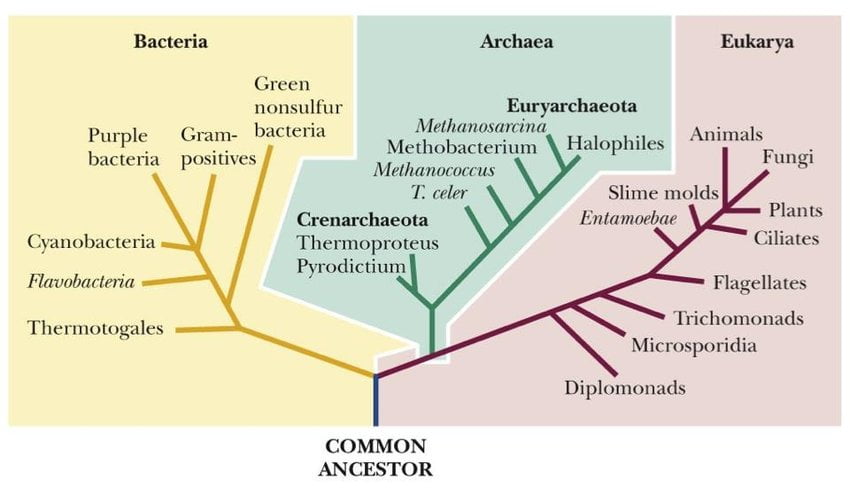
Carl Woese‘s Classification was introduced by Carl Woese in 1990. It classified the life forms into three-domains which include archaea, bacteria, and eukaryote. Introduction to Carl

Nomenclature is the set of rules and conventions which preside over the naming of taxa, while Classification is the grouping of organisms on the basis