Catalase and Oxidase tests are performed to check whether the given microorganism is aerobic or anaerobic.
Catalase Test –
The catalase enzyme protects the cell from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced during the metabolism of carbohydrates. The NADH, produced during metabolic reactions are oxidized to NAD in electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms, the oxygen acts like final electron acceptor. The negatively charged oxygen is highly reactive and froms Hydrogen peroxide (called as reactive oxygen species – ROS) and it is hazardous to cell. They are hazardous because they may alter the chemical nature of biomolecules like DNA, proteins and lipids.
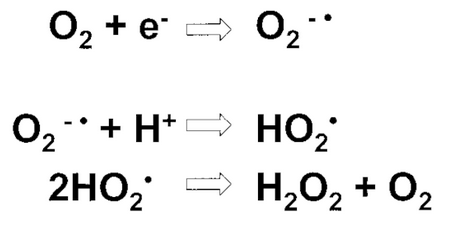
Catalase is an enzyme present in aerobic organisms that degrades hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen and protect from ROS.
Principle –
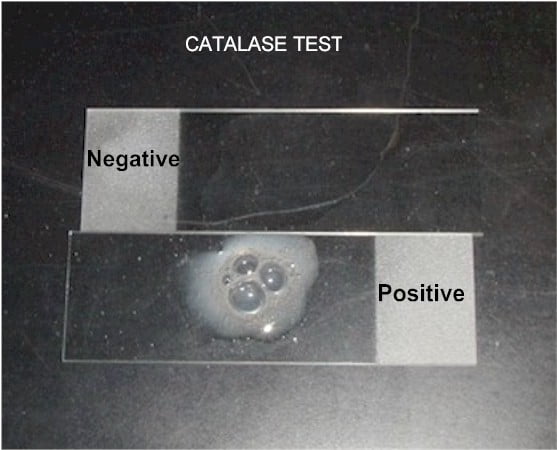
The catalase test is used to differentiate aerobic and anerobic microorganisms. The microorganisms are exposed to hydrogen peroxide. The cells with catalase positive degrade the hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. The test organism is exposed to hydrogen peroxide and observe the release of oxygen gas. The release of oxygen gas can be observed in the form of bubbling.
Requirements –
- Test Microorganism
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Slide
- Tooth pick
- Alcohol
Procedure –
- Wash and clean the microscopic slide.
- using toothpick, pick few colonies from agar culture.
- Place the colonies on the cleaned microscopic slide and make a smear.
- Put few drops of Hydrogen Peroxide onto the smear.
- If you observe bubbles, the test organism is catalase positive.
References –
https://asm.org/getattachment/00ce8639-8e76-4acb-8591-0f7b22a347c6/oxidase-test-protocol-3229.pdf