Carl Woese‘s Classification was introduced by Carl Woese in 1990. It classified the life forms into three-domains which include archaea, bacteria, and eukaryote.
Introduction to Carl Woese’s Classification
Life on earth was initiated 3.7 billion years ago. Evolution of the first life form resulted into diverse forms of living organisms from unicellular to multicellular. The natural evolution process includes formation of new species and extinction of the weak. As a biologist, it is important to know about the different life forms that are present on earth. To conduct systematic studies on different life forms, it is vital to classify them based on their characteristics. Classification allows us to organize and categorize different life forms. Recent studies have found that we have 8.7 million different species on earth from both, oceans and land. It is not only important to study the different life forms, but it is also important to discover and establish the evolutionary relationship among them. Classification is the best tool to conduct such studies.
History
Before Carl Woese’s proposal, the two-empire system was employed. He had proposed his ideas Philosophia Botanica. It had classified the living word in two empires- prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In the year 1990, Carl Woese proposed the 3-domain classification system to categorize all living forms. Domain is the highest rank in the taxonomic hierarchical classification. Based on the morphology and sequence differences of 16S ribosomal RNA, Carl Woese divided the diverse life form into major three domain namely Eubacteria, Archaebacteria and Eukaryotes. The 3-domain classification is also very useful to understand the phylogenetic relationship among the organisms.
Why 16S/18S rRNA is used for classification?
The ribosome contains small and large sub-units. In small sub-unit, 16S/18S rRNA is present. The function of 16S rRNA is to bind the shine-Dalgarno sequence of messenger RNA, whereas the 18S binds to the cap of mRNA. The reason for selecting 16S/18S rRNA is because of its conservative and variable sequence that allows to differentiate at species level and strain level. Moreover, the 16S/18S r RNA are ubiquitous in distribution and function, it means it is present in all species and have similar function. The phylogenetic relationship between two organisms can be predicted based on extent of similarity in ribosomal RNA. The Eukaryotes contains 18S RNA, but it also has some similar conservative sequence, as they are obtained from common ancestor. The 16S RNA served to the best tool for differentiating bacteria and archaebacteria.
What is Universal Phylogenetic Tree?
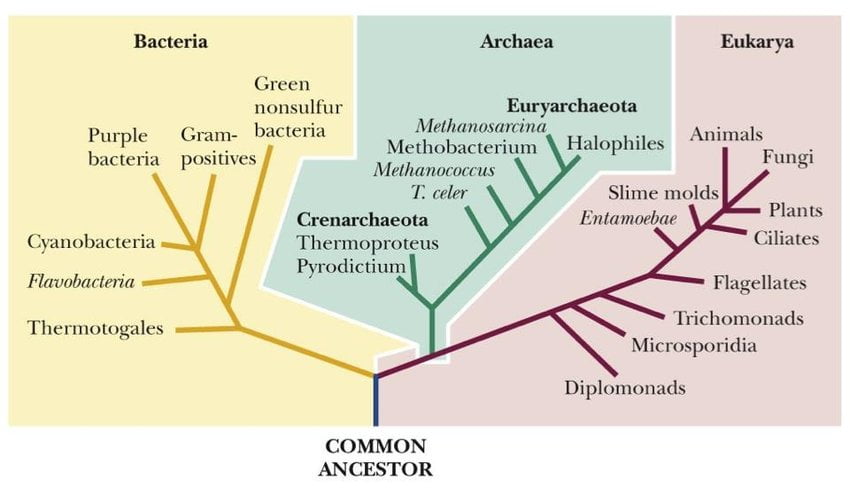
Carl Woese proposed universal Phylogenetic tree to depict the origin of all the simple and complex life forms. Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA) is considered an ancestor, and root of this Phylogenetic tree. The trunk of Phylogentic tree contains three branches as ‘Domains’ namely Bacteria, Archaebacteria and Eukaryotes.
Domain Bacteria:
- They are unicellular.
- They do not have defined nucleus.
- Bacteria lacks internal membrane bound organelle.
- Their cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan.
- In general, they are sensitive to antibiotics.
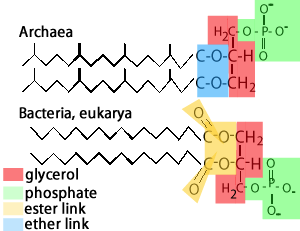
- The cell membrane is made from phospholipid bilayer, where the glycerol is linked to fatty acids by ester bonds. The involved fatty acids are unbranched and unsaturated type.
- Ribosome is of 70S type.
- The bacteria contain 16S rRNA.
- Operons are present.
- Histone proteins are not associated with DNA.
- Mode of reproduction is asexual.
- They grow in range of optimum temperature.
- The Bacteria domain contains phyla namely Proteobacteria, Cynaobacteria, Eubacteria, Chlamydias and Spirochetes etc.
- The mode of nutrition may be parasitic, free-living, autotrophic, chemoheterotrophic etc.
Domain Archaebacteria:
- They are called as ancient form of life.
- Archaebacteria are Unicellular and prokaryotic.
- They do not have defined nucleus.
- They lack membrane bound organelle.
- They lack peptidoglycan
- They are not much sensitive to bacterial antibiotics.
- Their cell membrane is made of phospholipid bilayer; the glycerol is linked to isoprene chains by ether bonds. The linked Fatty acids chains are branched and saturated type.
- Ribosome is of 70S type.
- The Archaebacteria contains 16S rRNA
- Operons are present.
- Histone proteins are associated with DNA.
- Mode of reproduction is asexual.
- They are extremophiles.
- They are non pathogenic.
Domain Eukaryotes:
- They includes both unicellular and multicellular types of organisms
- They have defined nucleus
- Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles.
- They lack peptidoglycan cell wall.
- They are not sensitive to bacterial antibiotics.
- The cell membrane is made of phospholipid bilayer. The glycerol is liked to fatty acids with ester bonds. The involved fatty acids are unbranched and unsaturated type.
- The ribosome is 80S type.
- They contain 18S rRNA.
- Operons are absent
- The DNA is associated with histone proteins.
- Mode of reproduction is both asexual and sexual.
- They are found in optimum temperature.
- It contains phyla namely Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
- The mode of nutrition could be heterotrophic, parasitic, saprophytic etc.
Difference between Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryotic cell membrane:
Bonus Activity for Carl Woese’s Classification:
| Characteristics | Bacteria Domain | Archaebacteria Domain | Eukaryotes Domain |
| Unicellular/Multicellular | |||
| Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic | |||
| Nucleus | |||
| Membrane Bound organelles | |||
| Operons | |||
| Histone Proteins | |||
| Cell membrane | |||
| Ribosome | |||
| Peptidoglycan | |||
| Mode of nutrition | |||
| Mode of reproduction |
If you liked this resource, please Like, Share, and Subscribe us for more content.


One thought on “Carl Woese’s Classification- Three Domain System”