Southern Hybridization is one of the nucleic acid Hybridization technique that allows us to identify similar sequence in DNA. It works on the principle of Watson and Crick complementary base pairing. The motive of identifying similar sequence is to find the extent of genetic relatedness or to find genetic variant. In hybridization method, a small fragment of DNA with known sequence called as probe are used to locate the sequence. The probes are either enzyme linked or have radio or fluorescent labelled. This technique was developed by Edward Southern in 1970.
In order to hybridize the DNA sample with probe, the complementary DNA strands needs to be separated. This can be achieved by treating the DNA sample with alkali.
Steps for DNA Hybridization –
Part A – DNA isolation and Southern Blotting
- Isolate the DNA from cell or an organism.
- Digest the isolated DNA with restriction enzyme.
- Load the digested DNA segments in the wells of agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. Due to the supply of electric field, the negatively charged DNA will start traveling towards positive electrode. The distance traveled by DNA segment is affected by its size.
- Eithium bromide intercalates with DNA segments and allow to visualize under UV.
- To denature the DNA segments of agarose gel, the gel is soaked in alkali.
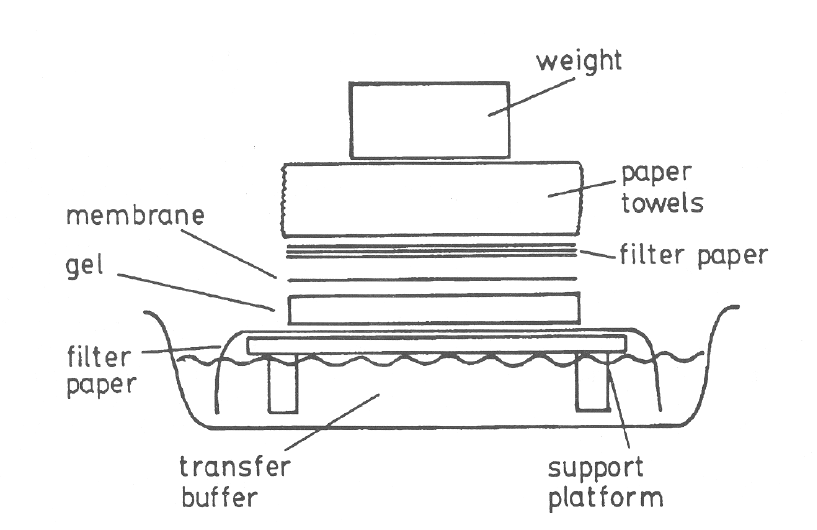
- The denatured segments are transferred on nylon or nitrocellulose membrane. The DNA gets transfer due gel to nitrocellulose due to the capillary action. The sequence of stacking is as follows-
- buffer
- sponge or support platform
- filter paper
- the gel containing the nucleic acid
- a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane
- more filter paper
- paper towels to catch the buffer that passed through all of the above
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/How-to-set-up-a-Southern-blot-transfer_fig2_237830208
Part B – DNA Hybridization –
- The Nylon filter paper with denatured DNA segments are incubated in prehybridization buffer. The buffer fills in the spots on the filter where the nucleic acid has not bound.
- The prehybridize nylon paper is exposed to probes.
- Keep it for incubation for 24 hours.
- The probe will bind to the complementary sequence and will glow or gives color.
- The non complementary probes can be washed using washing buffer.
- Autoradiography method is used to identify the location of labelled hybridized DNA segment.
Applications of Southern Hybridization –
- To identify the gene of interest.
- To identify the copy number of gene
- Identification of oncogene.
- To identify genetic variant.
- To identify infectious diseases.
- For DNA fingerprinting, where simple sequence repeats are used. Simple sequence repeats (SSR), or microsatellites, are ubiquitous in eukaryotic genomes. And the pattern of their presence is unique to respective organism (just like our palm and finger prints).
References –
https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/hybridization
https://www.bioinformatics.nl/molbi/SimpleCloningLab/blotting.htm


