Autoclave is an equipment used for sterilisation in Laboratories, Research Facilities and Educational Institutes, Pharmaceutical Companies, and certain industries. Over the past few months, owing to the pandemic, there has been a substantial rise in the usage & uses of this simple yet effective equipment.
Introduction:
Autoclave is essentially used for sterilization. Sterilization means inhibition or killing of microbes like bacteria, spores, fungi and virus etc. Hence, in Microbiology and Biotechnology, Autoclave is widely used for sterilization of media and glasswares etc. In autoclave, the method of killing the microbes is by the usage of moist heat and pressure. The Autoclave design and principle is referred from pressure cooker. And hence, in general, the autoclave is also called as pressure sterilizer. The portable autoclave can be place on working bench and called as benchtop autoclave or table top autoclave; the non portable autoclaves are placed on floor and called as floor autoclave. It is one of the most used equipments for sterilization in educational lab institutes, research institutes and pharmaceutical companies.
Autoclave was designed and invented by Charles Chamberland in the year 1879. The autoclaves that are commercially available now have better monitoring and safety systems, while working on the same original principle. For sterilization, it still remain a popular choice in Pharmaceutical companies, Educational institutes, Research Institutes, Dental clinics, Hospitals, and Tattoo industry.
In Hydrothermal Autoclave, the pressure can be set more than 2000 psi and more than 200°C, and are called as high pressure stem sterilizer.
Principle/Working:
The Autoclave works on steam under pressure principle. The high temperature and pressure ensures killing of microorganisms like virus, fungi, bacteria and heat resistant, spores. The high temperature and moist heat coagulate and denature microbial proteins and enzymes. it is usually set at 121°C and 15 lbs pressure for 15 minutes.
Procedure:
Steps in Autoclave Cycle-
- Boiling phase: The electric heat causes boiling of water and generate the steam. The produced steam replaces the trapped air by displacement.
- Rising temperature phase: The temperature rises and reaches up to the set level i.e. 121°C.
- Sterilization time: This is the time when microbes are killed.
- Release the pressure: The entrapped pressure is released by opening the valve.
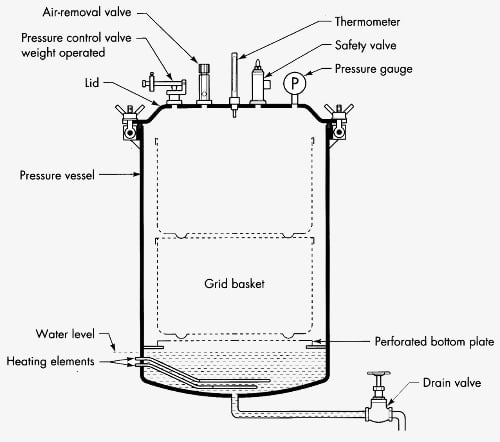
Construction/Parts:
The autoclave is made of following components/parts-
- Vessel or pressure chamber
- Lid or door
- Pressure gauge
- Pressure releasing unit (whistle)
- Safety valve
- Electrical heater
- Vessel/pressure chamber –
The vessel is made from stainless steel. The inner chamber is protected by outer jacket. The inner chamber is the place where we keep the autoclavable material for sterilization. The size of the chamber varies and selected based on the motive of use.
- Heater –
The electric heater is placed beneath the chamber. The electric heater working principle is similar to geezer. The electric heater start heating it causes boiling of water. The user need to maintained the water level as per the marking. Less water may cause burning and more water may lead to enter water in the experimental material.
- Lid/Door –
The Vessel mouth is covered by lid or door. It is also made from stainless steel. The lid allows trapping and retaining the heat and pressure inside the chamber and producing favorable environment for sterilization. The lid is tightly closed with the help of airtight screw.
- Pressure gauge –
It is present on the upper surface of lid. Its function is to indicate the level of pressure that is produced during autoclaving. It is vital part because it allows us to visually see the rise of pressure and alert for any forthcoming mishap hence it ensures the safety.
- Pressure releasing unit/whistle –
The whistle is placed on top of the surface of the lid, just like pressure cooker. The whistle allows us to release the pressure whenever required.
- Safety Valve:
It is present on the surface of the lid. Their function is to avoid catastrophic accident especially when pressure inside the chamber is uncontrollable.
IMAGE
Types of Autoclave:
There are different types of autoclave commercially available
1) Gravity Displacement: When the water boils and the steam is produced, it displaces the air by gravity with any mechanical assistance.
- Vertical type (designed in vertical shape)
- Horizontal type (designed in horizontal shape)
2) Pressure displacement: The displacement of air by steam is done mechanical assistance. It ensures better penetration of steam. It consists of steam generator and vacuum pump.
- Positive pressure displacement
- Negative pressure displacement
Uses of Autoclave:
Autoclave is used for the sterilization of media, glasswares, solutions, and numerous heat resistant laboratory accessories. It is also used to decontaminate the media before discarding.
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/sterilization/steam.html
http://www.frankshospitalworkshop.com/equipment/autoclaves_equipment.html
https://www.explainthatstuff.com/autoclaves.html
https://ehs.princeton.edu/book/export/html/380
https://labsafety.gwu.edu/autoclave-safety
Cappucino JG and Sherman N (1996). Microbiology, A Laboratory Manual 4th edition. Benjamin Cumings Inc. California.
https://tuttnauer.com/blog/autoclave-sterilization/what-is-an-autoclave
If you liked this resource, please Like, Share, and Subscribe us for more content.
Dr. Sangha Bijekar has 9 years of Teaching Experience at University level. She loves to get engage in teaching and learning process. She is into blogging from last two years. She intends to provide student friendly reading material. She is avid Dog Lover and animal rescuer. She is learned Bharatnatyam and Katthak Dancer. She is into biking and She also loves to cook.


