Chromosome is the compact structure of DNA. It is visible in different phases of mitosis and meiosis. Chromosome banding is an essential tool in Karyotyping. Karyotyping is a process of pairing and ordering all the chromosomes of the organism. The study is done to observe the abnormality of chromosomes. For chromosome staining, the cells are arrested at metaphase by using chemical like mytomycin C or colchisine. The different staining technique results in unique pattern of banding. According to Burkolder and Weaver, the different patterns of banding might be because of association of histone and non histone proteins. The histone proteins are always associated with DNA in uniform pattern whereas the non histone proteins are not uniform. This article discusses the most commonly used chromosome banding Techniques.
Types of Banding Techniques –
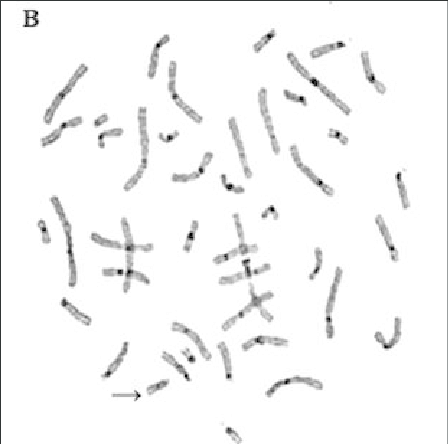
Q Banding –
- The Q stands for Quinacrine stain.
- It is one of the simplest method for staining chromosome.
- It is an intercalating agent and fluorescent compound (flourochrome).
- It is observed that quinacrine gets intercalate in Adenine and Thymine rich area. Hence, AT rich region appears bright whereas GC region appears dark.
- To observe the bands, chromosome are exposed to UV light.
- The bands appear bright in color against the dark background.
- On quinacrine staining, the particular chromosome shows characteristic patterns of banding and they are reproducible. Reproducible means particular chromosome shows similar pattern of banding every time. Quinacrine banding pattern is a specific characteristic of each chromosome, hence it is used for identification of chromosomes.
- It should be handle with handle as it is carcinogenic in nature.
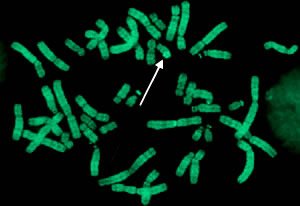
G Banding –
- G stands for Geimsa stain. The stain is mixture of cationic thiazine dyes, azure B, and anionic eosin dyes.
- It is also an intercalating agent.
- This is the second most commonly used method for staining chromosome.
- The Geimsa stain also binds to AT rich region and appears dark purple bands due to precipitation of eosin molecule with the thiazine molecules.
- Unlike Quinacrine stain, Geimsa is non flourescent hence UV light is not required to observe the bands.
- The G bands appears dark against background.
- On Geimsa staining, the particular chromosome shows characteristic patterns of banding and they are reproducible. Reproducible means particular chromosome shows similar pattern of banding every time. Quinacrine banding pattern is a specific characteristic of each chromosome, hence it is used for identification of chromosomes.
- The Giemsa staining technique may need pre-treatment with trypsin. The trypsin hydrolyzes the associated protein involved in DNA compaction.
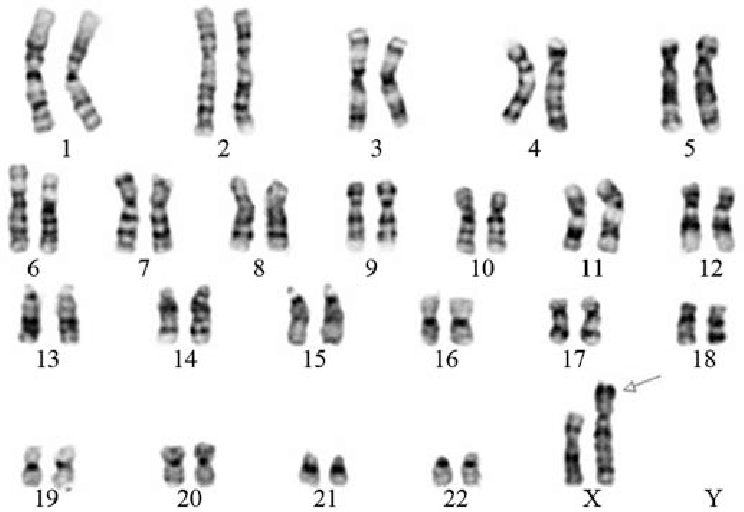
C-banding:
- C strands for Centromeric region. It is the central compact region of chromosome that separates p and q arm of chromosome.
- C banding is obtained by staining chromosome with Giemsa stain.
- It binds to AT rich region.
- The centromeric region is heterochromatin i.e. highly condensed. Hence, in order to stain, the chromosome need to be treated with acid, saline and alkali for denaturation. This causes depurination from certain region of DNA.
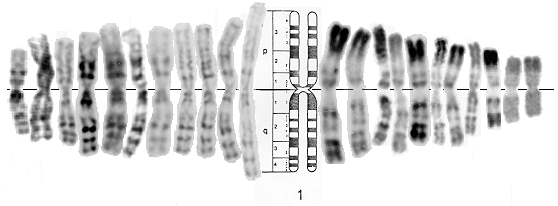
R Banding –
- R stands for reverse chromosome banding.
- R banding technique produces the bands that are reverse to Q and G bands (The At region appears light in color).
- R bands are obtained by preheating the chromosome at at 88°C in a buffer solution followed by staining with Giemsa stain (GC bonds melts around 105°C.
- Heating treatment causes denaturation of DNA at AT rich region but at GC region. Hence, the stain binds to GC region (euchromatin – less condensed DNA) and appears bright in color.
Conclusion –
The chromosome shows different pattern of bands based on the type of pretreatment and stain are used. Hence, the staining techniques are used for identification and comparison of chromosomes.
References –
- https://www.rpcau.ac.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/CHROMOSOME-CLASSIFICATION.pdf
- https://www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucapikr/projects/Ana_staining_LitRev.pdf
Dr. Sangha Bijekar has 9 years of Teaching Experience at University level. She loves to get engage in teaching and learning process. She is into blogging from last two years. She intends to provide student friendly reading material. She is avid Dog Lover and animal rescuer. She is learned Bharatnatyam and Katthak Dancer. She is into biking and She also loves to cook.

