Biosafety Cabinets are one of the most interesting safety equipments in a scientific lab. Often a part of sci-fi movies, these Biosafety Cabinets are enclosed workplace which are ventilated and provide protection to the user while handling contaminated or potentially contaminated micro-organisms.
Table Of Contents
- Introduction to Biosafety Cabinets
- BSC Class I
- BSC Class II
- BSC Class III
- Structural features of BioSafety Cabinets
Introduction to Biosafety Cabinets
“Safety” is a very well-known word; it is defined as, a condition of being protected from danger, risk, accident or injury. Biosafety means safety from biological agents like pathogenic microorganism or toxins. Biosafety includes rules, protocols, technologies, and practices. It is mandatory for all the laboratories to follow the Biosafety norms.

Based on the risk caused by biological agents, WHO classified biosafety into 4 levels and called as Biosafety Levels (BSL)-
| BSL | Risk | Diseases | Treatment |
| 1 | No | Does not cause any disease to human/animal | Not required |
| 2 | Moderate | Causes disease | Available |
| 3 | High | Causes serious diseases | Available |
| 4 | Extreme | Causes life threatening diseases | Not Available |
Based on the Biosafety level, working cabinets have been designed into 3 categories to fulfill the need of mentioned risk level and they are called as Biosafety cabinets. The biosafety cabinets are complemented with HEPA filters for directional flow of sterile air. The biosafety cabinets provide protection from harmful biological agent to the user. The Cabinets also reduced the probability of contamination. The Biosafety Cabinet (BSC) classification is as follows-
| Classification | Type | Biosafety level | Purpose |
| BSC class I | – | 1 | For low to moderate risk |
| BSC class II | A1, A2, B1, B2 | 2 | Moderate to high |
| BSC class III | – | 3 & 4 | High |
BSC Class I –
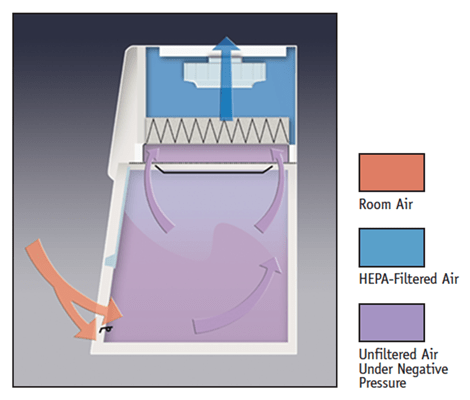
It is the most basic design among the biological safety cabinets. BSC I provide protection to user and environment but not to sample. The plenum protects the user. When user is working on any biological agent in the BSC, the agent might be moving in the cabinet in the form of aerosol. While exiting from cabinet, these aerosols pass through HEPA filter. The filter traps the biological agent and decontaminated air is exhausted. BSC I does not protect the sample from the biological agents present in the air of room. Hence, in BSC I there is more possibility of contamination of sample.
BSC Class II –
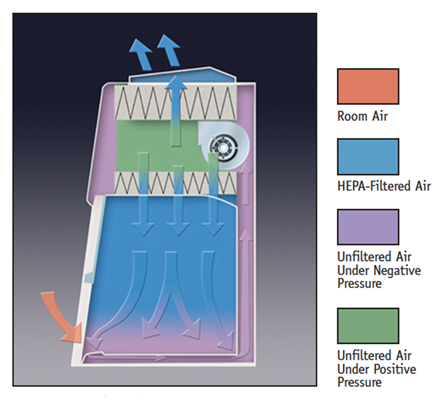
It is advanced form of BSC I that provides protection to user, environment and Sample. The downward flow system of HEPA filter provides protection to experimental sample. The decontaminate airflow from HEPA filter on the working bench of cabinet protecting sample. BSC II protects environment by similar mechanism that is followed in BSC I by suing HEPA filtered exhaust. The further types of BSC II are based on the HEPA filtered exhaust air; in different following types the extent of recirculation of air varies.
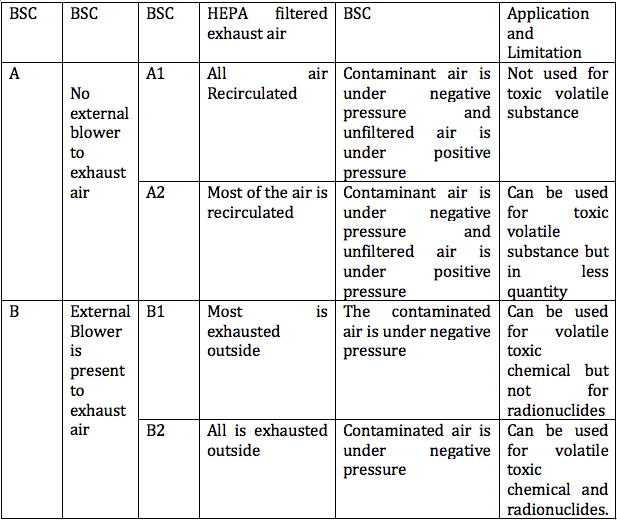
Diagrams


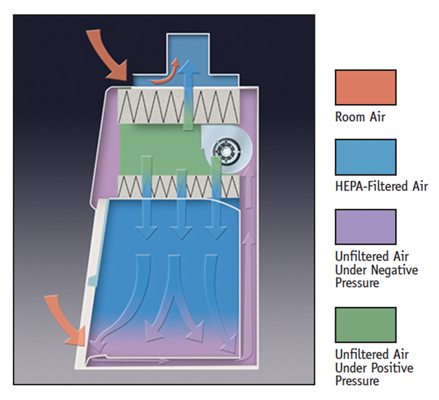
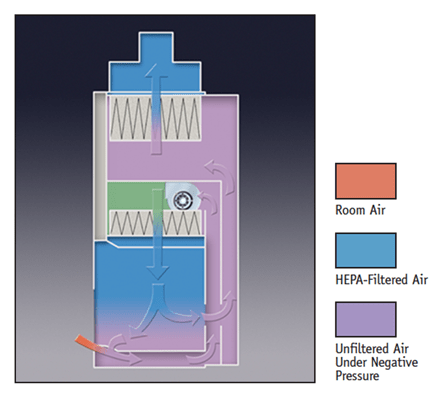
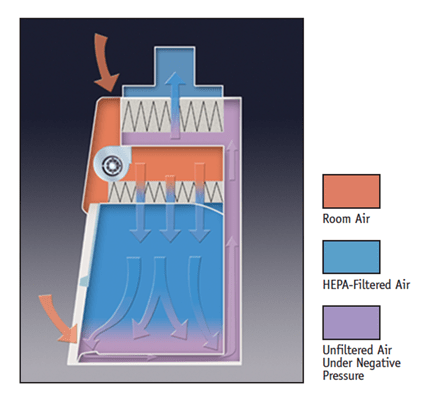
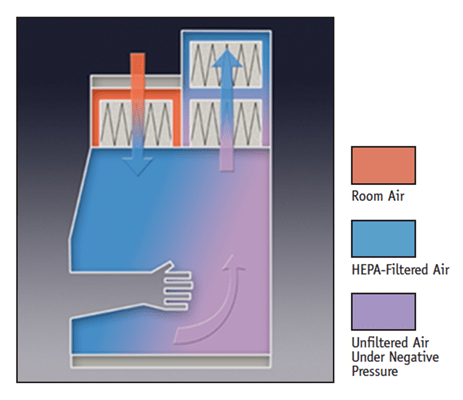
BSC III –

This type of Biosafety cabinets are totally enclosed and associated with attached rubber gloves for user’s hands. This class is used for working on the biological agent, which are at biosafety risk level 3 and 4. This cabinet offers highest level of protection to person, environment, and experimental material.
Structural features of BioSafety Cabinets –
- The sidewalls of the BSC working bench are made of stainless steel.
- The BSC has visible light of 800 lux.
- It also contains UV lamp for sterilization (User should not come in to direct contact of UV light).
- The unit has user-friendly microprocessor regulatory system that displays the required parameter digitally and allows the user to control it.
- The BSC are accompanied with sensors for external factors like heat, dust and moisture.
- High efficiency HEPA filter should be assembled with 0.2 to 0.3 μ.
- The BSC should not make much noise.
- It is should be easy to clean and decontaminate.
Need more help? Click here to read more.